What is a Computer-Use Agent?
Understanding AI agents that can see and interact with computer interfaces
A computer-use agent is an AI system that can perceive, understand, and interact with graphical user interfaces (GUIs) just like a human user would, as well as execute code and shell commands in isolated environments. These agents can "see" the screen and perform actions through simulated mouse and keyboard inputs, or run scripts and programs directly to accomplish tasks.
How Computer-Use Agents Work
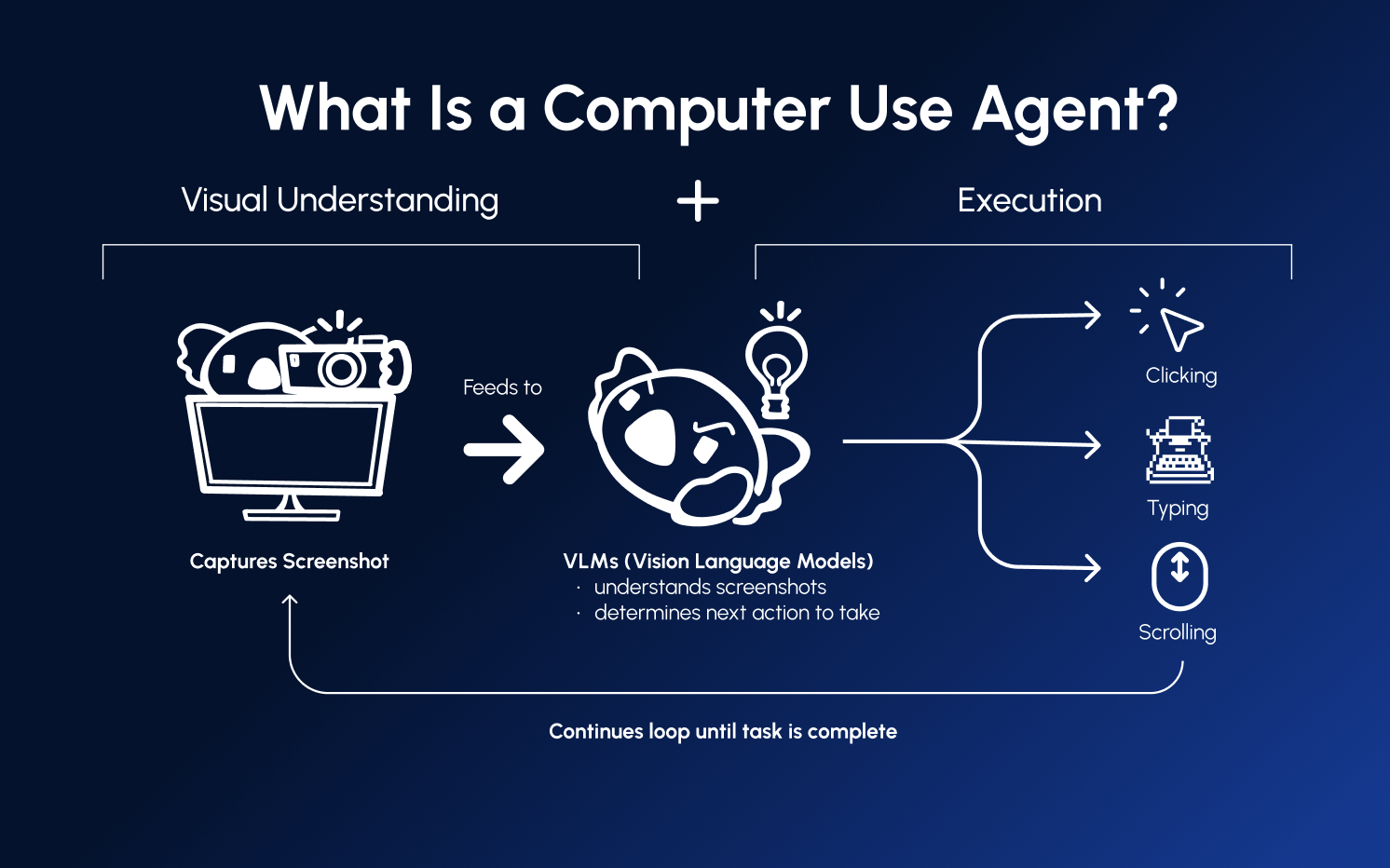
Computer-use agents operate through a continuous loop:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. OBSERVE │
│ Take a screenshot of the screen │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 2. UNDERSTAND │
│ Vision-language model analyzes │
│ the screenshot and current goal │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 3. DECIDE │
│ Determine the next action: │
│ click, type, scroll, etc. │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 4. ACT │
│ Execute the action on the computer │
└──────────────────┬──────────────────────┘
│
▼
Loop back to 1This cycle repeats until the agent completes its goal or determines it cannot proceed.
Key Components
Vision-Language Models (VLMs)
At the core of computer-use agents are vision-language models—AI models that can process both images and text. These models:
- Identify UI elements (buttons, text fields, menus)
- Read text on screen
- Understand spatial relationships
- Reason about what actions to take
Popular VLMs for computer use include Claude (Anthropic), GPT-4V (OpenAI), and Gemini (Google).
Grounding Models
Grounding models specialize in precisely locating UI elements on screen. Given a description like "the Submit button," they return exact pixel coordinates. Examples include:
- UI-TARS
- GTA-1
- Moondream
Planning Models
Planning models handle high-level reasoning—deciding what to do next given the current state and goal. They're typically large language models that excel at:
- Breaking down complex tasks into steps
- Handling errors and unexpected situations
- Maintaining context across multiple actions
Composed vs. End-to-End Agents
End-to-End Agents
A single model handles both understanding and action selection:
Screenshot → [Single VLM] → ActionPros: Simpler architecture, lower latency Cons: May sacrifice accuracy in either perception or planning
Composed Agents
Separate models for grounding and planning:
Screenshot → [Grounding Model] → UI Elements → [Planning Model] → ActionPros: Best-in-class performance for each capability Cons: Higher complexity, potentially higher cost
Cua supports both approaches, letting you choose based on your requirements.
Challenges in Computer Use
Building effective computer-use agents involves solving several challenges:
- Coordinate accuracy - Clicking the right pixel matters
- Timing - Waiting for pages to load, animations to complete
- Error recovery - Handling popups, errors, and unexpected states
- Context management - Remembering what's been done across many steps
- Safety - Preventing unintended actions on real systems
Cua addresses these challenges with sandboxed environments, optimized agent loops, and built-in safety mechanisms.
Next Steps
- Learn about Desktop Sandboxes where agents run safely
- Set Up a Sandbox to build your first agent
Was this page helpful?